The myelin sheath is found surrounding axons of both the central and peripheral nervous systems. Axons may be either myelinated or unmyelinated. In myelinated axons, the sheath is arranged with small gaps known as the Nodes of Ranvier. Action potentials are generated at these nodes as the majority of the axon’s ion channels are located here. This article will discuss the myelin sheath, its effects on the transmission of action potentials, and relevant clinical conditions.
The Myelin Sheath
Myelin is a lipid-rich substance that surrounds some axons within the central and peripheral nervous systems. The sheath is formed by the wrapping of multiple layers of the cellular membrane (mainly lipoprotein) of the myelin-producing cells around the axon. In the central nervous system (CNS) these cells are the oligodendrocytes, and in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) these cells are Schwann cells.
A single oligodendrocyte can myelinate up to 50 axons, whereas a single Schwann cell is only able to myelinate a single axon. Individual Schwann cells can each cover around 100 micrometers of an axon – meaning that it takes around 10,000 Schwann cells to myelinate a meter of the axon. As mentioned previously, the gaps left between areas of myelination are known as the Nodes of Ranvier.
Little is known about the exact process of myelination. It begins in utero – early in the third trimester. Although there is very little myelin present at birth, it progresses rapidly during infancy. This occurs in line with the development of various cognitive and motor skills. Myelination continues throughout adolescence and into early adulthood, following which the process is largely complete.
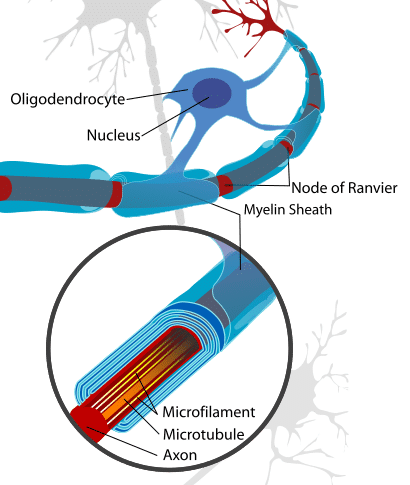
Fig 1 – Diagram showing the myelin sheath surrounding an axon in the CNS – with associated oligodendrocyte.
Effects of the Myelin Sheath
The myelin sheath conveys certain properties that increase the speed at which axons are able to conduct the action potential.
Membrane Resistance
Myelin has a high membrane resistance:
- Resistance – the degree to which a membrane prevents or facilitates free movement of ions. A low resistance membrane allows lots of ion movement, and a high resistance membrane does not.
This occurs because the myelin sheath inhibits ion movement along the insulated area of the axon, encouraging the diffusion of ions along the axon to reach the next node. At the node, the high concentration of ion channels enables rapid depolarisation and action potential generation.
Membrane Capacitance
Myelin also reduces the capacitance of the axon:
- Capacitance – the ability of an electrical system to store charge or the charge required to initiate an action potential/electrical impulse. The low capacitance conveyed to an axon by myelination means that a lower change in ion concentration is required to initiate an axon potential.
These factors mean myelinated axons are able to conduct action potentials much faster than unmyelinated axons. This is via saltatory conduction, where action potentials appear to ‘jump’ between Nodes of Ranvier.
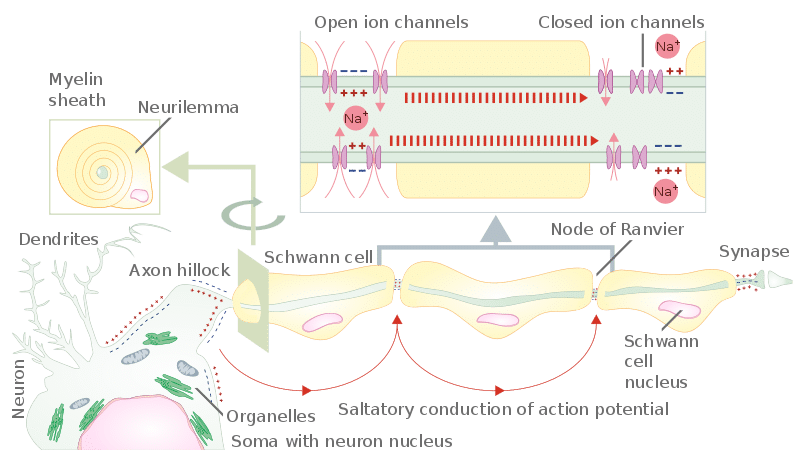
Fig 2 – Diagram to show how the myelin sheath results in saltatory conduction of an action potential along an axon.
Clinical Relevance – Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Guillain-Barré Syndrome is a rapid onset of muscle weakness, caused by autoimmune damage to the peripheral nervous system. The exact cause is unknown, but the underlying mechanism is damage to the myelin sheath of peripheral nerves by the body’s immune system.
Initial symptoms usually include changes to sensation or pain and muscle weakness. These begin distally in the feet and hands and then typically spread proximally to the arms and upper body.
The symptoms develop over varying time frames, from hours to over a few weeks. If the respiratory muscles are affected, this disorder can become life-threatening and require mechanical ventilation.
Treatment is with supportive care, plasmapheresis, and intravenous immunoglobulins. Whilst the majority of patients undergo recovery, this can take weeks to years. Additionally, around a third of patients will experience some residual weakness.
